Designing Effective Hybrid Learning Environments
Facilitating Collaboration and Communication Across Diverse Learners
The hybrid learning model presents distinct challenges for student interaction and teamwork. Establishing effective communication pathways for both physical and online participants is essential. Solutions may include dedicated digital discussion areas, collaborative work platforms, or virtual small-group sessions. Encouraging active student involvement in these interactive spaces helps build a sense of academic community and shared purpose.
Addressing the varying requirements of different learners remains crucial. Students demonstrate differing technological proficiencies and learning approaches. Offering multiple communication options – including video calls, text-based messaging, and email – accommodates these differences. Creating opportunities for face-to-face interaction and relationship-building among students further promotes an inclusive and cooperative learning atmosphere.
Creating a Supportive and Inclusive Learning Community
A strong sense of belonging is particularly important in hybrid educational environments. Providing regular opportunities for student-student and student-instructor interaction helps build community connections. This might involve virtual social spaces, online study groups, or scheduled in-person meetings. Consistent communication regarding expectations, available support, and community standards from instructional staff remains vital.
Fostering an atmosphere of mutual respect and inclusion is equally important. This requires creating environments where students feel comfortable sharing ideas, asking questions, and participating in discussions. Encouraging students to contribute their unique perspectives and experiences enhances the learning environment while strengthening community bonds. Addressing potential participation barriers – such as technology access or digital skills – further promotes inclusivity.
Assessing and Adapting the Hybrid Model
Understanding the Hybrid Learning Landscape
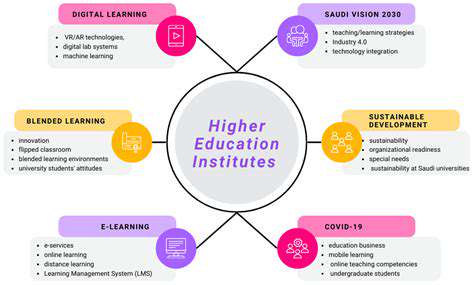
The growing popularity of hybrid instruction models combines the strengths of online and traditional classroom teaching to accommodate diverse learner requirements. Successful implementation demands thorough consideration of each modality's advantages and limitations, requiring deep understanding of the specific educational context including available technological resources, student characteristics, and faculty capabilities. This comprehensive understanding is necessary to optimize both instructional components, creating more effective and engaging learning experiences.
Recognizing individual learning differences is particularly important. While some students excel in structured classroom settings, others perform better in online environments. Well-designed hybrid models address this diversity through flexible options that allow students to engage with material in ways that best suit their learning preferences.
Adapting Existing Curricula for Hybrid Delivery
Converting traditional courses to hybrid formats requires significant pedagogical redesign. Simply digitizing existing lectures proves insufficient; instructors must strategically restructure curricula to capitalize on the unique benefits of both delivery modes. This involves careful integration of interactive online components, self-paced learning modules, and collaborative assignments to maximize engagement and knowledge retention across all learning environments.
Effective technology integration remains paramount. Selecting appropriate learning platforms, utilizing interactive digital tools, and implementing communication systems are critical for successful hybrid instruction. Special attention must be given to accessibility features and technological support services to ensure equitable access for all participants.
Assessment methodologies require similar adaptation to align with hybrid structures. Traditional testing methods may need supplementation with online evaluations, practical projects, or digital presentations. The transition to hybrid learning also necessitates reconsideration of evaluation criteria and grading frameworks to maintain academic standards while accommodating diverse learning approaches.
The inherent flexibility of hybrid education enables customized learning experiences. This may involve adjusting instructional pacing and structure to better meet individual student needs. Faculty must demonstrate willingness to modify teaching approaches and incorporate varied instructional strategies to optimize student engagement and learning outcomes.
Assessing the Impact and Evolving the Model
Continuous evaluation of hybrid program effectiveness is essential for ongoing improvement. Systematic collection of data regarding student participation, academic performance, and satisfaction levels helps identify areas requiring refinement. This information should guide adjustments to instructional content, technology utilization, and teaching strategies over time. Regular feedback mechanisms involving instructors, students, and administrators are crucial for developing successful hybrid learning environments.
Thorough analysis of collected data enables institutions to identify successful program elements and areas needing enhancement. This cyclical improvement process creates dynamic educational environments that evolve with changing participant needs. Ultimately, comprehensive assessment protocols ensure hybrid models remain responsive and effective in meeting contemporary educational requirements.