Gamification vs Game Based Learning: Understanding the Difference
What is Gamification?
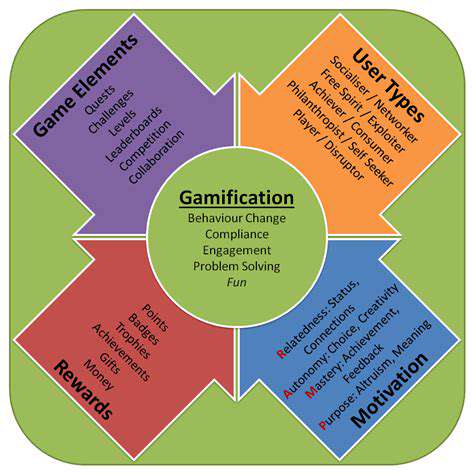
Understanding the Core Concept
Gamification represents the integration of playful design components into everyday activities. Rather than being limited to entertainment, this method enhances participation across diverse sectors including corporate training and academic settings. The human psyche naturally responds to structured challenges and visible progress indicators, making this approach universally effective.
At its foundation, this methodology capitalizes on our psychological predisposition toward achievement-oriented activities. Interactive elements like scoring systems, achievement markers, and competitive rankings transform routine tasks into dynamic experiences. Organizations implementing these strategies often observe measurable improvements in participation metrics and task completion rates.
Key Elements and Mechanics
Successful implementation requires thoughtful selection of interactive components. Progress trackers, recognition symbols, and comparative rankings serve as fundamental building blocks, each influencing participant behavior through distinct psychological pathways.
The architecture of advancement plays equally vital role. Clearly articulated objectives paired with real-time performance indicators establish what psychologists term the accomplishment cycle - a self-reinforcing pattern that maintains participant involvement over extended durations.
Tiered difficulty structures and mission-based frameworks further enrich the experience, providing participants with graduated challenges that match their developing competencies. This scaffolding approach prevents disengagement while promoting skill advancement.
Applications and Benefits
The versatility of this approach spans multiple industries. Educational institutions report improved attendance and comprehension when incorporating interactive elements into their curricula, while corporate training programs demonstrate higher retention rates through simulated scenarios.
Participation enhancement stands as the most immediately observable advantage. When routine activities incorporate elements of play, both the frequency and quality of engagement typically increase. This phenomenon explains why customer retention programs and employee training initiatives increasingly adopt these methods.
Cognitive scientists note improved information retention when learning occurs through interactive formats. The combination of multisensory stimulation and emotional engagement creates neural pathways that facilitate long-term memory formation, particularly beneficial in academic and professional development contexts.
Impact on Student Engagement and Motivation
Impact on Student Engagement
Traditional lecture formats often struggle to maintain student attention, whereas interactive methodologies demonstrate consistently higher engagement metrics. The incorporation of achievement tracking and incremental challenge structures aligns with developmental psychology principles regarding sustained focus.
Healthy competition, when properly structured through comparative performance displays, can stimulate academic effort without creating negative stress responses. Educators report that students participating in these enhanced learning environments demonstrate improved assignment completion rates and classroom participation.
Motivation Through Rewards and Challenges
The human brain responds powerfully to achievement recognition, a principle leveraged effectively through tiered reward systems. Digital accomplishment markers function similarly to academic honors, triggering dopamine responses that reinforce positive behaviors.
Beyond extrinsic motivators, well-designed systems cultivate internal drive by aligning educational milestones with personal growth narratives. Students begin viewing academic progress as a journey of self-improvement rather than obligation, fundamentally shifting their relationship with learning.
Personalized Learning Experiences
Adaptive difficulty algorithms allow educational content to respond dynamically to individual performance patterns. This customization addresses the historical challenge of single-pace instruction failing to accommodate diverse learning velocities within classroom settings.
Enhanced Knowledge Retention
Neuroscientific research confirms that information acquired through active participation demonstrates significantly higher recall rates than passive reception. The multisensory nature of interactive learning environments creates multiple neural access points for information retrieval.
Increased Collaboration and Communication
Team-based challenges within these systems mirror professional workplace dynamics, providing students with early exposure to collaborative problem-solving. Educators observe that these shared experiences often break down social barriers and create more inclusive classroom environments.
Development of Critical Thinking Skills
Scenario-based challenges require participants to analyze variables, predict outcomes, and adjust strategies - all essential components of higher-order cognition. This active processing distinguishes surface learning from deep conceptual understanding, preparing students for complex real-world decision-making.
Addressing Diverse Learning Styles
The multimodal nature of interactive systems accommodates various cognitive processing preferences simultaneously. Visual learners benefit from graphical progress displays, auditory learners from narrative components, and kinesthetic learners from interface interactions, creating a universally accessible educational framework.
Choosing the Right Approach
Defining Gamification
This methodology transforms ordinary processes through strategic implementation of achievement markers and progress indicators. Unlike full-scale simulations, it enhances existing frameworks without requiring complete system overhauls. Retail loyalty programs exemplify this approach, where purchase tracking and reward milestones influence consumer behavior through psychological reinforcement.
Understanding Game-Based Learning
Comprehensive educational simulations represent a distinct approach, constructing entire knowledge acquisition frameworks within interactive environments. These systems immerse learners in scenario-based challenges where academic content becomes integral to narrative progression and gameplay mechanics.
Key Differences in Design
The fundamental distinction lies in implementation scope. Enhancement strategies modify existing systems through layered interactive elements, while comprehensive simulations build educational content directly into their core architecture. This structural variance determines both development resources required and potential depth of learner immersion.
Focus and Objectives
Process enhancement prioritizes participation metrics and completion rates, valuable in corporate training and customer engagement contexts. Comprehensive simulations target specific competency development, making them preferable for complex skill acquisition in fields like medical training or technical education.
Impact on Motivation and Engagement
Both methodologies demonstrate efficacy in maintaining participant involvement, though through different mechanisms. Layered enhancements provide continuous micro-feedback, while immersive simulations offer macro-level narrative progression. The optimal choice depends on whether the primary need involves routine task engagement or complex skill mastery.
Considerations for Implementation
Resource allocation represents a primary decision factor. Process enhancements typically require less developmental overhead and integrate more easily with existing systems. Comprehensive simulations demand greater initial investment but may yield deeper educational outcomes for complex subject matter.
Measurable Outcomes and Evaluation
Assessment protocols must align with implementation objectives. Process enhancements track quantitative metrics like participation frequency and completion rates. Comprehensive simulations require qualitative assessment of skill demonstration and knowledge application, often utilizing scenario-based testing frameworks.
Read more about Gamification vs Game Based Learning: Understanding the Difference
Hot Recommendations
- Attribution Modeling in Google Analytics: Credit Where It's Due
- Understanding Statistical Significance in A/B Testing
- Future Proofing Your Brand in the Digital Landscape
- Measuring CTV Ad Performance: Key Metrics
- Negative Keywords: Preventing Wasted Ad Spend
- Building Local Citations: Essential for Local SEO
- Responsive Design for Mobile Devices: A Practical Guide
- Mobile First Web Design: Ensuring a Seamless User Experience
- Understanding Your Competitors' Digital Marketing Strategies
- Google Display Network: Reaching a Broader Audience