From Crisis to Innovation: The Hybrid Learning Paradigm Shift
Personalized learning is rapidly transforming the educational landscape, moving away from a one-size-fits-all approach to a more tailored, student-centered model. This shift acknowledges the diverse learning styles, paces, and needs of individual students, recognizing that each learner possesses unique strengths and challenges. This approach fosters a deeper understanding and engagement with the subject matter, ultimately leading to improved academic outcomes.
By adapting curriculum and instruction to meet individual needs, personalized learning empowers students to take ownership of their learning journey. This empowers students with a more active and engaging role in their education, fostering a love of learning and promoting self-directed learning skills.
Tailoring Instruction to Individual Needs
A key aspect of personalized learning is tailoring instruction to address the specific learning needs of each student. This involves assessing each student's strengths, weaknesses, learning style, and preferred methods of engagement to create a customized educational path. This personalized approach ensures that students receive the appropriate support and challenges to optimize their learning.
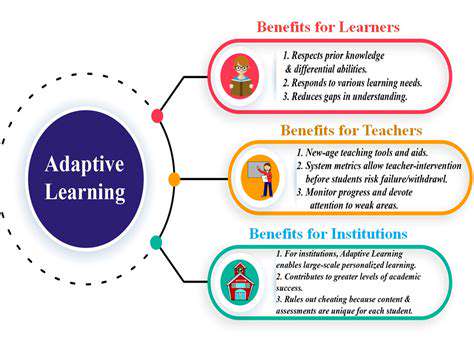
This individualized approach can involve a variety of strategies, from differentiated instruction to adaptive learning platforms. These methods allow for a more dynamic and effective learning experience, leading to better understanding and mastery of the subject matter.
Technology's Role in Personalized Learning
Technology plays a crucial role in facilitating personalized learning, providing educators and students with tools and resources to tailor the learning experience. Adaptive learning platforms, for instance, can adjust the difficulty and pace of content based on individual student performance, providing a highly customized learning environment. These innovative technologies empower teachers to provide targeted support and challenges, ultimately maximizing the learning potential of each student.
Interactive online resources, educational games, and digital simulations are among the tools that enhance engagement and cater to diverse learning preferences. These technologies can provide opportunities for students to explore concepts at their own pace and in ways that resonate with their individual learning styles.
The Impact on Student Engagement and Motivation
Personalized learning fosters a sense of ownership and engagement in students. When students feel that their learning journey is tailored to their specific needs, they are more likely to become actively involved in the process. This increased engagement leads to higher motivation, a more positive attitude towards learning, and a greater desire to succeed.
By recognizing and addressing individual learning styles and preferences, personalized learning can significantly improve student motivation and engagement. This, in turn, leads to a more positive and productive learning environment for all students.
Assessment and Feedback in Personalized Learning
Personalized learning necessitates a shift in assessment practices, moving away from standardized testing towards more formative and continuous assessment. This involves gathering data on student understanding and progress throughout the learning process to inform instructional adjustments. Regular feedback and reflection are essential components in this approach, helping students understand their strengths and weaknesses and identify areas requiring further development.
The Future of Personalized Learning
The future of personalized learning is bright, with ongoing advancements in technology and pedagogical approaches continuing to shape this evolving paradigm. As technology continues to advance, personalized learning will become even more sophisticated, enabling educators to provide students with highly tailored and engaging learning experiences. Further research and development in this area will undoubtedly lead to innovative methods and tools that will empower students to achieve their full potential.
The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning holds great promise in creating even more sophisticated and personalized learning environments in the future.
Adapting the Curriculum and Redefining Classroom Dynamics
Reimagining Learning Spaces
The current crisis has highlighted the limitations of traditional learning spaces. Adapting the curriculum necessitates a reimagining of these spaces, moving beyond the confines of a single, static classroom. Flexible learning environments, incorporating collaborative zones, quiet study areas, and technology integration hubs, can foster a more dynamic and engaging learning experience. This shift requires careful consideration of student needs and preferences, ensuring accessibility and inclusivity for all learners.
Moving beyond the rigid structure of a typical classroom also means rethinking the physical layout. Creating spaces that encourage interaction and collaboration, rather than simply passive reception of information, is crucial. This could involve incorporating breakout rooms, designated project areas, and even outdoor learning spaces, depending on the resources and context of the school or institution. These changes must be underpinned by a commitment to supporting teachers in utilizing these spaces effectively.
Enhancing Digital Literacy and Competency
The pandemic accelerated the adoption of digital tools in education, forcing educators and students to adapt to remote learning environments. This shift demands a more proactive approach to digital literacy, equipping students with the skills to navigate and utilize technology effectively in their learning journey. This includes not only technical proficiency but also critical thinking skills around information evaluation and responsible digital citizenship.
Beyond basic computer skills, digital competency now encompasses the ability to use various online platforms, manage digital resources, and collaborate effectively in virtual settings. This requires a comprehensive curriculum approach that integrates digital literacy into all subjects, not just as a standalone skill but as an essential tool for learning and communication. Training teachers on utilizing these tools effectively and safely in the classroom is equally crucial.
Fostering Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving
The challenges presented by the crisis underscore the importance of fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills in students. Traditional teaching methods often prioritize rote memorization and passive learning, but the current context demands a more active and engaged approach. Curriculum adjustments need to incorporate opportunities for students to analyze information, evaluate different perspectives, and develop creative solutions to complex problems.
Developing these skills is not merely about teaching students how to think critically; it's about creating a learning environment that encourages exploration, experimentation, and intellectual curiosity. This requires a shift in pedagogy, moving away from a teacher-centered approach towards a more student-centric model where students actively participate in their learning process. By integrating real-world applications and case studies into the curriculum, we can effectively cultivate these essential skills for success in the future.